All of the following are on an unclassified balance sheet – As the unclassified balance sheet takes center stage, this opening passage invites readers into a realm of financial clarity. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of balance sheet components, unraveling the significance of current and non-current assets, liabilities, and equity.
Brace yourself for an enlightening exploration of the financial landscape.
Current Assets

Current assets are assets that are expected to be converted into cash within one year or the operating cycle of the business, whichever is longer. They are typically found on the unclassified balance sheet under the heading “Current Assets”.Current assets include:
- Cash and cash equivalents
- Accounts receivable
- Inventory
- Prepaid expenses
- Short-term investments
Current assets that are not included on the unclassified balance sheet include:
- Investments in affiliated companies
- Loans to officers and employees
- Property, plant, and equipment held for sale
Distinguishing between current and non-current assets is important because it provides information about the liquidity of a company. Current assets are more liquid than non-current assets, which means that they can be converted into cash more quickly.
Non-Current Assets: All Of The Following Are On An Unclassified Balance Sheet
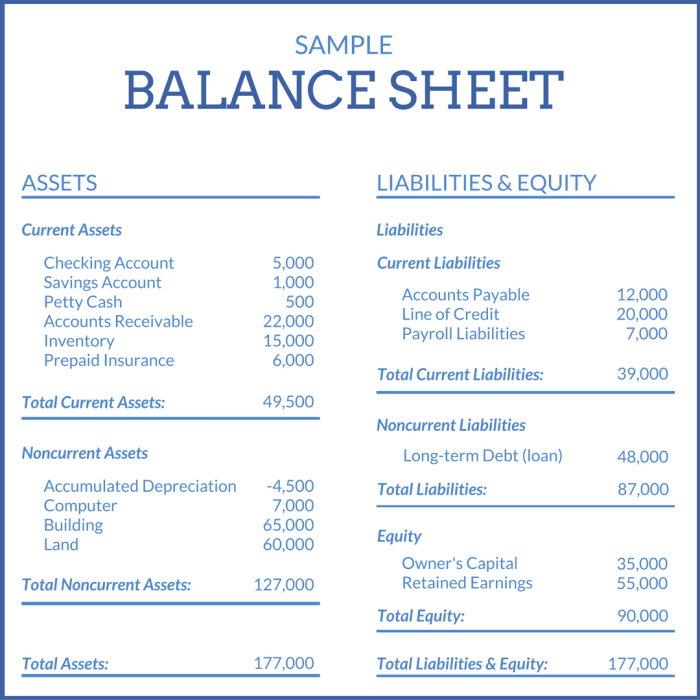
Non-current assets are assets that are not expected to be converted into cash within one year or the operating cycle of the business, whichever is longer. They are typically found on the unclassified balance sheet under the heading “Non-Current Assets”.Non-current
assets include:
- Property, plant, and equipment
- Intangible assets
- Investments
- Long-term loans
Non-current assets are important because they represent the long-term investments that a company has made. They can provide a source of future income and growth.There are different methods that can be used to value non-current assets. The most common methods are:
- Historical cost
- Current cost
- Fair value
The method that is used to value non-current assets will depend on the specific circumstances.
Liabilities
Liabilities are debts that a company owes to other entities. They are typically found on the unclassified balance sheet under the heading “Liabilities”.Liabilities can be classified as either current or non-current. Current liabilities are debts that are due within one year or the operating cycle of the business, whichever is longer.
Non-current liabilities are debts that are due after one year or the operating cycle of the business.Examples of current liabilities include:
- Accounts payable
- Short-term loans
- Accrued expenses
Examples of non-current liabilities include:
- Long-term loans
- Bonds
- Deferred income taxes
It is important to distinguish between liabilities and equity. Liabilities are debts that a company owes to other entities, while equity represents the ownership interest in a company.
Equity
Equity is the ownership interest in a company. It is typically found on the unclassified balance sheet under the heading “Equity”.Equity can be divided into two main categories:
- Shareholder equity
- Retained earnings
Shareholder equity represents the investment that shareholders have made in a company. Retained earnings represent the profits that a company has accumulated over time.Equity is important because it represents the net worth of a company. It can be used to measure the financial health of a company and to assess its ability to meet its obligations.
Answers to Common Questions
What is the purpose of an unclassified balance sheet?
An unclassified balance sheet provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time, categorizing assets, liabilities, and equity without further subclassification.
What are the main components of an unclassified balance sheet?
The main components of an unclassified balance sheet include current assets, non-current assets, current liabilities, non-current liabilities, and equity.
What is the difference between current and non-current assets?
Current assets are expected to be converted into cash within one year, while non-current assets are expected to be held for a longer period.