Photosynthesis what’s in a leaf pogil – Photosynthesis: What’s in a Leaf POGIL embarks on an enthralling journey, unraveling the intricate workings of life’s fundamental process. Delving into the heart of a leaf, we uncover the secrets that sustain our planet, illuminating the path towards a sustainable future.
From the intricate structure of a leaf to the remarkable function of chloroplasts, we explore the mechanisms that drive photosynthesis, the lifeblood of our planet. This activity unravels the mysteries of light-dependent reactions and the Calvin cycle, shedding light on the remarkable interplay between light energy and carbon dioxide.
Photosynthesis: What’s in a Leaf?
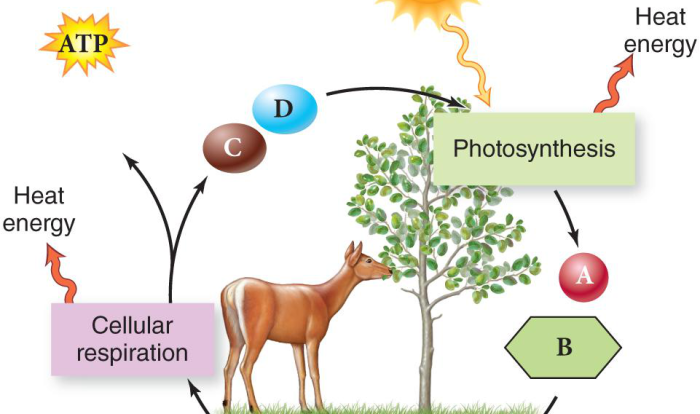
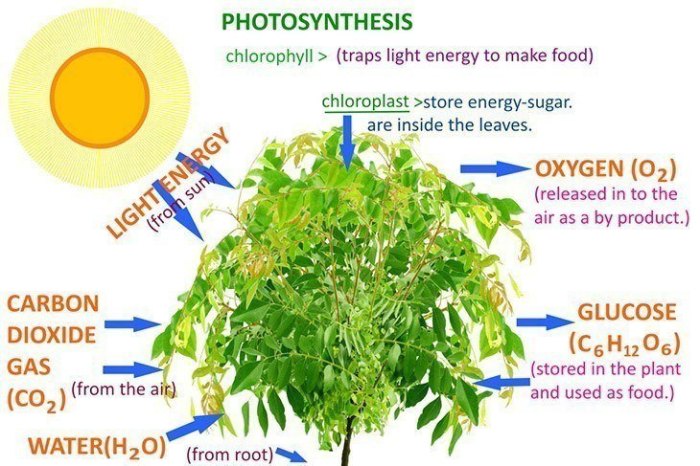
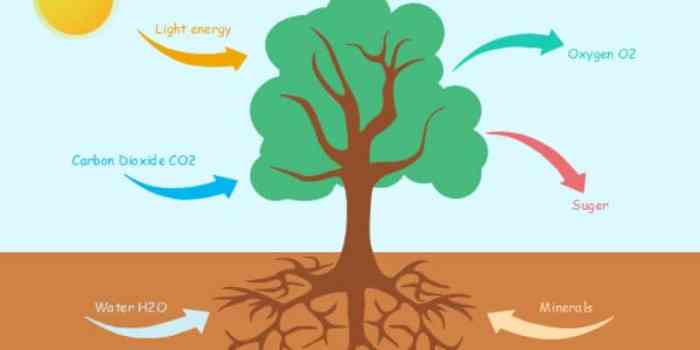
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants and other organisms use sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. It is a vital process for life on Earth, as it provides the food and oxygen that we need to survive.
The purpose of the “Photosynthesis: What’s in a Leaf” POGIL activity is to help students understand the structure of a leaf and the process of photosynthesis.
Leaf Structure
A leaf is a thin, flat organ that is attached to a plant stem. Leaves are the primary site of photosynthesis. They are covered by a waxy cuticle that helps to protect them from water loss and damage.
The epidermis is the outermost layer of the leaf. It is made up of a single layer of cells that are tightly packed together. The epidermis helps to protect the leaf from water loss and damage.
The mesophyll is the middle layer of the leaf. It is made up of a loose network of cells that contain chloroplasts. Chloroplasts are organelles that contain chlorophyll, a green pigment that absorbs light energy from the sun.
The vascular tissues are the innermost layer of the leaf. They are made up of xylem and phloem. Xylem transports water and minerals from the roots to the leaves. Phloem transports glucose from the leaves to the rest of the plant.
Chloroplasts
Chloroplasts are organelles that are found in the mesophyll cells of leaves. They are the site of photosynthesis. Chloroplasts are surrounded by a double membrane. The inner membrane is folded into thylakoids. Thylakoids are flattened sacs that contain chlorophyll.
Chlorophyll is a green pigment that absorbs light energy from the sun. This light energy is used to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. The hydrogen is used to reduce carbon dioxide into glucose. The oxygen is released into the atmosphere.
Light-Dependent Reactions: Photosynthesis What’s In A Leaf Pogil
The light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis are a series of chemical reactions that use light energy to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. The hydrogen is used to reduce NADP+ to NADPH. The oxygen is released into the atmosphere.
The light-dependent reactions take place in the thylakoids of the chloroplasts.
Calvin Cycle
The Calvin cycle is a series of chemical reactions that use the hydrogen and NADPH from the light-dependent reactions to reduce carbon dioxide into glucose. The Calvin cycle takes place in the stroma of the chloroplasts.
The Calvin cycle is a cyclic process. This means that the products of the cycle are used to regenerate the reactants.
Factors Affecting Photosynthesis

The rate of photosynthesis is affected by a number of factors, including light intensity, temperature, and water availability.
- Light intensity: The rate of photosynthesis increases as the light intensity increases.
- Temperature: The rate of photosynthesis increases as the temperature increases, up to a certain point. After this point, the rate of photosynthesis decreases.
- Water availability: The rate of photosynthesis decreases as the water availability decreases.
Applications of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is used in a variety of applications, including agriculture, medicine, and energy production.
- Agriculture: Photosynthesis is used to produce food for humans and animals.
- Medicine: Photosynthesis is used to produce drugs and other medical products.
- Energy production: Photosynthesis is used to produce biofuels, such as ethanol and biodiesel.
FAQ Section
What is the primary function of photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants and other organisms convert light energy into chemical energy, producing glucose and releasing oxygen as a byproduct.
What is the role of chlorophyll in photosynthesis?
Chlorophyll is a green pigment found in chloroplasts that absorbs light energy, which is then used to drive the reactions of photosynthesis.
What factors can affect the rate of photosynthesis?
Factors such as light intensity, temperature, water availability, and carbon dioxide concentration can influence the efficiency of photosynthesis.